



Summary of U.S. Government
Expenditures and Income
Total U.S. Government Budget (2024)
Total Spending: $6.75 trillion
Total Revenue: $4.9 trillion
Deficit : $1.85 trillion
National Debt (End of 2024): ~$36 trillion
Mandatory Spending - (See Explanation)
Government Expenditures : $6.75 Trillion
1. Social Programs & Public Assistance
•
Social Security: $1.46 trillion
•
Medicare & Medicaid (Healthcare Programs):
o
$912 billion
•
Veterans Benefits & Assistance: $210.9 billion
•
Other Social Welfare Programs: $1,482 per person
(average amount of tax dollars allocated per taxpayer
toward veteran and military benefits.
o
(includes SNAP, housing, and disability benefits)
Discretionary Spending (See Explanation)
2. Department of Defense Budget (2025): $883 billion
•
Veterans Affairs & Military Benefits: $3,367 per
person
3. Legislative Branch (Congress & Senate)
•
Salaries for Senators & Congress Members:
o
$94.28 million
•
Senate Offices & Committees: $68.36 million
4. Executive Branch
•
Department of Health & Human Services (HHS):
o
$130.7 billion (Discretionary)
o
$1.7 trillion (Mandatory)
•
Department of Commerce:
o
$11.4 billion (Discretionary)
o
$4 billion (Mandatory)
•
Department of Labor: $97.5 billion (See Description)
5. Federal Judiciary Budget (FY 2024): $9.1 billion
•
Salaries for Judges: $796 million (Mandatory)
•
Court Operations: $6.4 billion (Discretionary)
o
(salaries, expenses, clerks' offices, probation services)
•
Support Staff: Included in court operations and defender
services (Discretionary)
o
$1.5 billion for federal defenders.
•
Other Expenses (Facilities, IT, & Other Judicial Services):
o
$400 million (court security, IT modernization, and other
o
infrastructure costs) (Discretionary)
6. Other Federal Spending - Over $1 trillion annually (EST)
(Discretionary)
•
Infrastructure: Road and bridge projects.
•
Education: Federal student aid, grants,
o
and K-12 programs.
•
Research: Scientific funding (e.g., NIH, NASA, NSF).
•
Interest Payments on National Debt
o
(Over $1 trillion annually) (Mandatory)
Government Income (Revenue) $4.9 Trillion
2. Other Sources
•
Tariffs & Customs Duties
•
Fees & Fines (passports, national parks, etc.)
•
Federal Reserve Transfers (profits from bond
purchases)
United States Income - Expenditure


USA - News
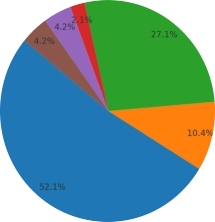











Income Taxes 52.1%
Corporate Taxes 10.4%

Payroll Taxes 27.1%
Excise Taxes 2.1%
Tariffs & Fees 4,2%
Fed. Transfers 4.2%



Government Income (Revenue) $4.90 Trillion
Government Expenditures : $6.75 Trillion
Deficit : $1.85 Trillion

How the Government Covers Its Deficit and
Where the Fed Gets Money
In 2024, the U.S. government spent $6.75 trillion
but only collected $4.9 trillion in revenue (mainly
from taxes). This created a $1.85 trillion deficit,
meaning the government had to borrow to cover
the shortfall.
How the Government Borrows Money
To cover the deficit, the government sells Treasury
bonds, bills, and notes (IOUs) to investors, banks,
and even foreign countries. Buyers of these bonds
lend money to the government in exchange for
future repayment with interest.
How the Federal Reserve Helps
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a role by buying
these Treasury bonds when needed, injecting
money into the economy. Unlike a regular bank,
the Fed creates money digitally,
Where Does the Fed Get Money?
The Fed does not print cash to buy government
debt. Instead, it adds money electronically to
banks’ accounts, increasing the amount of money
in the financial system. This helps keep interest
rates low, making borrowing cheaper.
Long-Term Effects
The national debt grows as deficits pile up year
after year. The Fed can later sell these bonds to
remove excess money from the economy.
If too much money is created, it can lead to
inflation, meaning prices rise.
Effect on National Debt
The deficit adds to the national debt, which
reached nearly $36 trillion by the end of 2024.
This means the government continues to pay
interest on borrowed money, further increasing
future financial obligations.
Copyright © 2025 globalgrype.com
All rights Reserved
Mandatory Spending:
Automatically funded based on eligibility laws. ie:
Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, SNAP
Discretionary Spending:
Requires Congress to approve funding each year
Defense, Education, Transportation, FBI, NASA
Department Of Labor
Employment and Training
Administration (ETA):
•
Oversees workforce development programs,
including job training and unemployment
insurance.
Occupational Safety and
Health Administration (OSHA):
•
Ensures safe and healthful working conditions
by setting and enforcing standards.
Wage and Hour Division (WHD):
•
Enforces federal labor laws related to
minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor.
Employee Benefits Security
Administration (EBSA):
•
Protects the integrity of pensions, health
plans, and other employee benefits.
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS):
•
Collects and analyzes essential economic
data, including employment and inflation
statistics.






















